Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women of childbearing age. PCOS is a condition that disrupts ovulation and can make women sterile. PCOS is a leading cause of infertility, but with proper management and treatment, a successful pregnancy is possible for most women with PCOS. This article examines how PCOS leads to infertility, the role of hormonal imbalance, and how treatment is achievable, for example, through drugs such as Duphaston.
Understanding PCOS and Its Impact on Ovulation
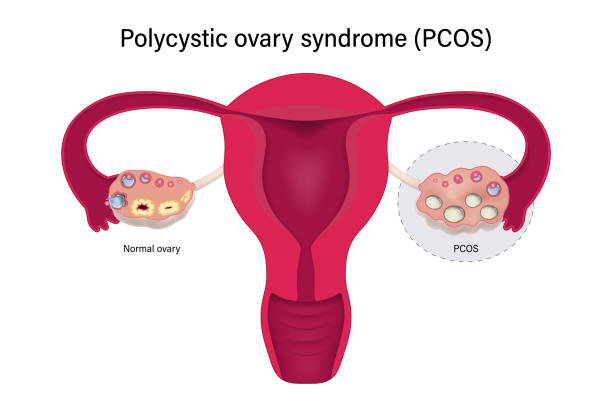
PCOS affects the ovaries’ functioning by causing a disruption in reproductive hormones. Normally, the ovaries release eggs every month with a process called ovulation. In PCOS women, however, ovulation is disrupted by the hormonal imbalance, causing irregular or absent menstrual periods. This occurs due to the overproduction of androgens (male hormones) and disruption of the balance of estrogen and progesterone.
One of the traditional characteristics of PCOS is a large number of small fluid-filled sacs (cysts) on the ovaries. These cysts are not actually cysts but immature follicles with eggs that do not progress further and are hence not released. This prevents ovulation, and it is hard to conceive.
Hormonal Imbalances That Result in Infertility
Several hormonal imbalances in PCOS result in infertility:
1. Elevated Androgen Levels (Hyperandrogenism)
Women with PCOS have higher androgen levels such as testosterone. Elevated androgens interfere with the maturation and release of eggs from ovaries, such that ovulation stops and becoming pregnant becomes complicated.
2. Insulin Resistance
In the majority of women with PCOS, the body does not respond properly to insulin. Therefore, it results in hyperinsulinemia with increased secretion of insulin levels stimulating the secretion of androgens by ovaries. There occurs a mix-up of too many androgens and too much insulin producing anovulation as well as abnormal menstrual bleeding.
3. Disruption of LH and FSH
Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) regulate ovulation. In PCOS, the LH is generally too elevated in comparison to FSH, causing distorted follicular growth and inability to ovulate.
4. Low Progesterone Levels
After ovulation, the hormone progesterone is employed to maintain the uterine lining in preparation for a fertilized egg to be implanted. But since women with PCOS do not usually ovulate, their progesterone levels don’t increase, leading to irregular cycles and difficulty conceiving.
How PCOS Causes Infertility
The interplay of the foregoing hormonal imbalances affects the normal reproductive cycle in several ways:
- Irregular Ovulation: Without regular ovulation, no egg is released to be fertilized by the sperm.
- Anovulatory Cycles: The majority of women who have PCOS experience cycles that have absolutely no ovulation whatsoever, and hence conception is pretty much impossible.
- Poor Egg Quality: Even where ovulation actually occurs, the eggs are usually of poor quality due to the hormonal imbalances.
Thin Uterine Lining
Inadequate progesterone may result in an underdeveloped uterine lining, where it is difficult for an implanted fertilized egg to develop and sustain pregnancy.
Treatment of PCOS Infertility
The good news is that PCOS-caused infertility can usually be treated with lifestyle changes and medication. Some of the effective treatments are as follows:
1. Lifestyle Changes
- Weight Management: Losing excess pounds of 5-10% can normalize menstrual cycles and improve ovulation.
- Healthy Diet: A diet of whole foods, rich in fiber, lean protein, and healthy fats, might help to induce hormonal balance.
- Exercise: Exercise lowers insulin resistance and overall reproductive health.
2. Medications to Induce Ovulation
Several medications are prescribed to stimulate ovulation in women with PCOS:
- Clomiphene Citrate: A first-line treatment that induces the ovaries to release eggs.
- Letrozole: Typically prescribed for women who are unresponsive to Clomid, Letrozole works by reducing estrogen levels, increasing FSH production, and improving ovulation.
- Metformin: A medication for diabetes that sensitizes the body to insulin, which restores ovulation in PCOS patients with insulin resistance.
3. Progesterone Therapy with Duphaston
Duphaston (Dydrogesterone) is a synthetic progesterone that is commonly prescribed to women with PCOS to control menstrual cycles and ensure pregnancy.
- Turning Back Menstrual Cycles: Duphaston controls menstrual periods in females who experience infrequent or absent periods due to PCOS.
- Supporting Pregnancy: Since most women with PCOS have lower levels of progesterone, Duphaston will ensure that the uterine lining remains intact and the risk of miscarriage early on is avoided.
- Increasing Fertility Treatment: It is often used with ovulation induction treatment to enable a healthy pregnancy.
4. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
In women who are not pregnant on their own with medication, assisted reproductive techniques such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in-vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended. These procedures have the ability to circumvent part of the ovulatory challenge of PCOS and enhance the likelihood of pregnancy.
Treatment of PCOS for Long-Term Fertility
PCOS cannot be cured, but effective management can improve fertility outcomes. Long-term management comprises:
- Regular Checkup: Tracking menstrual cycle and ovulation by basal body temperature or ovulation predictor tests.
- Healthy Weight: Minimal weight loss can greatly improve fertility.
- Reduced Stress: High levels of stress can worsen hormonal imbalance, and it becomes even harder to conceive.
Conclusion
PCOS is a complex hormonal disorder that significantly impairs a woman’s fertility. With appropriate treatment and management, however, most women with PCOS can reverse infertility and have a successful pregnancy. Medications like Duphaston are an essential component of having regular menstrual cycles and maintaining early pregnancy. If you have PCOS and infertility, visiting a healthcare provider for a personalized treatment program is essential. By implementing lifestyle changes and subjecting themselves to medical therapies, PCOS women can improve their reproductive health and improve the chances of getting a baby.

